Cho ∫ 1 m x + m 2 - 8 d x = 2 3 3 x + 1 + C . Tính giá trị của tích phân I = ∫ m - 2 e x ln 2 x
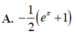
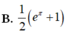
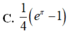
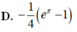
1) Cho phuong trinh x+m / x+1 + x-2 / x = 2. De phuong trinh vo nghiem thi: A. m = 1 hoac m = 3 B. m = -1 hoac m = -3 C. m =2 hoac m=-2 D. m = -1/3 hoac m = 1/2
Cho pt : x2 + 2(m+1)x - 2m4 +m2 =0
a, giải pt khi m=1
b, tìm m để pt có 2 nghiệm x1, x2 sao cho (m-1)x1 +x1x2 + (m-1)x2 = -1
Lời giải:
a)
Khi $m=1$ thì pt trở thành:
$x^2+4x-1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+2)^2=5\Rightarrow x+2=\pm \sqrt{5}$
$\Rightarrow x=-2\pm \sqrt{5}$
b)
Để pt có 2 nghiệm pb $x_1,x_2$ thì:
$\Delta'=(m+1)^2-(-2m^4+m^2)>0\Leftrightarrow 2m^4+2m+1>0(*)$
Áp dụng định lý Vi-et: \(\left\{\begin{matrix} x_1+x_2=-2(m+1)\\ x_1x_2=-2m^4+m^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi đó:
$(m-1)x_1+x_1x_2+(m-1)x_2=-1$
$\Leftrightarrow (m-1)(x_1+x_2)+x_1x_2=-1$
$\Leftrightarrow -2(m-1)(m+1)+(-2m^4+m^2)=-1$
$\Leftrightarrow -2m^4-m^2+3=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (1-m^2)(2m^2+3)=0$
$\Rightarrow m^2=1\Rightarrow m=\pm 1$
Thay vào $(1)$ thấy 2 giá trị đều thỏa mãn.
cho pt x\(^2\) +2(m-1)x-m=0(1) m là tham số.
a) giải pt (1) với m=1.
b) tìm giá trị của m sao cho các nghiệm x\(_1\), x\(_2\)của pt (1)thỏa mãn
2(x\(_1\)+x\(_2\))-3x \(_1\)x\(_2\)+9=0
a: Thay m=1 vào pt, ta được:
\(x^2-1=0\)
=>(x-1)(x+1)=0
=>x=1 hoặc x=-1
b: \(\text{Δ}=\left(2m-2\right)^2-4\cdot\left(-m\right)\)
\(=4m^2-8m+4+4m\)
\(=4m^2-4m+4\)
\(=4\left(m^2-m+1\right)\)
\(=4m^2-4m+1+3=\left(2m-1\right)^2+3>0\)
Do đó: Phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt
Ta có: \(2\left(x_1+x_2\right)-3x_1x_2+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\cdot\left[-2\left(m-1\right)\right]-3\cdot\left(-m\right)+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4\left(m-1\right)+3m+9=0\)
=>-4m+4+3m+9=0
=>13-m=0
hay m=13
a, Thay m = 1 ta được
\(x^2-1=0\Leftrightarrow x=1;x=-1\)
b,
Theo Vi et \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-2\left(m-1\right)\\x_1x_2=-m\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(-4\left(m-1\right)+3m+9=0\Leftrightarrow-m+13=0\Leftrightarrow m=13\)
Tìm m sao cho phương trình có 1 nghiệm cho trước và tìm nghiệm còn lại
a) 2x2 - (m + 3)x + m - 1 = 0 (x1 = 3)
b) (m + 1)x2 - 2(m-1)x + m - 2 = 0 (x1 = 2)
thế x1vào bt =>\(2\times3^2-\left(m+3\right)\times3+m-1=0\Leftrightarrow18-3m-9+m-1=0\)
<=>8 - 2m=0 <=>m=4
thế 4 vào bt 2x2 - (m + 3)x + m - 1 = 0 <=>2x2-7x+3=0 <=>\(\left(x-3\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=3\)hoặc x=0.5 thỏa mãn
b tương tự
bài 1: cho hàm số y = 2x3 - 3(2m+1)x2 + 6m(m+1)x + 1. Chứng minh rằng y' = 0 luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt với x2 - x1 không phụ thuộc vào m.
bài 2: cho hàm số y = [(m-1)x3]/3 + mx2 + (3m-2)x. tìm m để y' ≥ 0 với mọi x thuộc R
bài 3: cho hàm số y = [x2 + (m-1)x + 2 ]/(x-1). tìm m để y' = 0 có hai nghiệm thỏa mãn x1.x2 = -3
bài 4: cho hàm số y = (x2+ mx - 1)/(x-1) tìm m để y' ≥ 0 với mọi x ≠ 1.
bài 5: cho hàm số y = mx3 + 3mx2 - (m-1)x - 1. tìm m để y' = 0 không có hai nghiệm phân biệt.
Câu 1.Cho pt (m-3)x2-2(m+2)x+m+1=0 (1)
a, Tìm m để pt (1) có nghiệm.Tím nghiệm x2 biết x1=2
b,Tìm m để pt (1)có 2 nghiệm x1,x2 thỏa mãn \(\dfrac{1}{x_1}+\dfrac{1}{x_2}=10\)
Câu 2.Cho pt (m-2)x2+2(m+1)x+m-1=0
a, Tìm m để pt có 2 nghiệm cùng dấu
b, Tìm m để pt có 2 nghiệm x1,x thỏa mãn x13+x23=64
Câu 3.Tìm m để pt
2x2+2(2m+1)x+2m2+m-1=0 có 2 nghiệm x1, x2 sao cho \(\dfrac{x_1^2}{x_2^2}+\dfrac{x^2_2}{x^2_1}>7\)
a) để phương trình có 2 nghiệm : \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-3\ne0\\\Delta'\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-3\ne0\\\left(m+2\right)^2-\left(m-3\right)\left(m+1\right)\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ne3\\6m+7\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ne3\\m\ge\dfrac{7}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
thay \(x_1=2\) vào phương trình ta có :
\(4\left(m-3\right)-4\left(m+2\right)+m+1=0\Leftrightarrow m=19\)
áp dụng hệ thức vi ét ta có : \(x_1+x_2=\dfrac{2\left(m+2\right)}{m-3}=\dfrac{2\left(21\right)}{16}=\dfrac{21}{8}\)
\(\Rightarrow x_2=\dfrac{21}{8}-x_1=\dfrac{21}{8}-2=\dfrac{5}{8}\)
vậy ....................................................................................................
b) áp dụng hệ thức vi ét ta có : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=\dfrac{2\left(m+2\right)}{m-3}\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{m+1}{m-3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
ta có : \(\dfrac{1}{x_1}+\dfrac{1}{x_2}=10\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x_1+x_2}{x_1x_2}=10\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\left(m+2\right)}{m-3}:\dfrac{m+1}{m-3}=10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2m+4}{m+1}=10\Leftrightarrow2m+4=10m+10\Leftrightarrow m=\dfrac{-3}{4}\left(L\right)\)
vậy không có m thỏa mãn điều kiện bài toán .
câu 2) a) để phương trình có 2 nghiệm cùng dấu \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-2\ne0\\\Delta'\ge0\\p>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-2\ne0\\\left(m+1\right)^2-\left(m-2\right)\left(m-1\right)\ge0\\\dfrac{m-1}{m-2}>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ne2\\5m-1\ge0\\\left(m-1\right)\left(m-2\right)>0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ne2\\m\ge\dfrac{1}{5}\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}m>2\\m< 1\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow m>2\) vậy \(m>2\)
b) áp dụng hệ thức vi ét ta có : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=\dfrac{-2\left(m+1\right)}{m-2}\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{m-1}{m-2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
ta có : \(x_1^3+x_2^3=64\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^3-3\left(x_1x_2\right)\left(x_1+x_2\right)=64\)
\(\left(\dfrac{2m+2}{2-m}\right)^3+6\left(\dfrac{m-1}{m-2}\right)\left(\dfrac{m+1}{m-2}\right)=64\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(-2m-2\right)^3}{\left(m-2\right)^3}+\dfrac{6\left(m-1\right)\left(m+1\right)\left(m-2\right)}{\left(m-2\right)^3}=64\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-8m^3-24m^2-24m-8+6m^2-12m^3-6m+12}{m^2-6m^2+12m-8}=64\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-20m^3-18m^2-30m+4}{m^3-6m^2+12m-8}=64\)
\(\Leftrightarrow84m^3-402m^2+798m-516=0\)
giải nốt nha .
câu 3 : để phương trình có 2 nghiệm . \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m+1\right)^2-2\left(2m^2+m-1\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2+4m+1-4m^2-2m+2\ge0\Leftrightarrow2m+3\ge0\Leftrightarrow m\ge\dfrac{-3}{2}\)
áp dụng hệ thức vi ét ta có : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-2m-1\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{2m^2+m-1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
ta có : \(\dfrac{x_1^2}{x_2^2}+\dfrac{x_2^2}{x_1^2}>7\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x_1^4+x_2^4}{x_1^2x_2^2}>7\) \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x_1^2+x_2^2\right)^2-2x_1^2x_2^2\left(x_1^2+x_2^2\right)}{x_1^2x_2^2}>7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(\left(x_1+x_2\right)-2x_1x_2\right)^2-2x_1^2x_2^2\left(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2\right)}{x_1^2x_2^2}>7\)
thế vào giải ....
1. Xác định tham số m sao cho PT :
2x2 - (3m +1 )x + m2 - m -6 = 0 có 2 nghiệm trái dấu
2. Cho PT : mx2 + 2(m-4)x +m +7 = 0
Tìm m để 2 nghiệm x1 và x2 thỏa mãn hệ thức : x1 - 2x2 = 0
3. Cho PT : x2 + ( 4m +1 )x +2(m -4 ) = 0
Tìm hệ thức liên hệ giữa x1 và x2 sao cho chúng không phụ thuộc vào m
1. \(2x^2-\left(3m+1\right)x+m^2-m-6=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac=\left[-\left(3m+1\right)\right]^2-4.2.\left(m^2-m-6\right)=9m^2+6m+1-8m^2+8m+48=m^2+14m+49=\left(m+7\right)^2\ge0\forall m\)
=> PT có 2 nghiệm với mọi m.
Theo Vi-ét, ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}S=x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=\dfrac{-\left[-\left(3m+1\right)\right]}{2}=\dfrac{3m+1}{2}\\P=x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=\dfrac{m^2-m-6}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Để pt có 2 nghiệm trái dấu \(\Leftrightarrow P< 0\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{m^2-m-6}{2}< 0\Leftrightarrow m^2-m-6< 0\Leftrightarrow-2< m< 3\)
Vậy -2<m<3 thì pt có 2 nghiệm trái dấu.
2. \(mx^2+2\left(m-4\right)x+m+7=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac=\left[2\left(m-4\right)\right]^2-4.m.\left(m+7\right)=4\left(m^2-8m+16\right)-4m^2-28m=4m^2-32m+64-4m^2-28m=-60m+64\)
Để pt có 2 nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow-60m+64\ge0\Leftrightarrow m\le\dfrac{16}{15}\)
=> PT có 2 nghiệm với \(m\le\dfrac{16}{15}\)
Theo Vi-ét, ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}S=x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=\dfrac{-2\left(m-4\right)}{m}=\dfrac{-2m+8}{m}\\P=x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=\dfrac{m+7}{m}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có hpt: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=\dfrac{-2m+8}{m}\\x_1-2x_2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=\dfrac{-2m+8}{m}\\x_1=2x_2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\left(2x_2+x_2\right)=-2m+8\\x_1=2x_2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3mx_2=-2m+8\\x_1=2x_2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_2=\dfrac{-2m+8}{3m}\\x_1=2.\dfrac{-2m+8}{3m}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay \(x_1;x_2\) vào P:
\(\dfrac{2\left(-2m+8\right)}{3m}.\dfrac{-2m+8}{3m}=\dfrac{m+7}{m}\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\left(8-2m\right)^2}{9m^2}-\dfrac{m+7}{m}=0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\left(64-32m+4m^2\right)}{9m^2}-\dfrac{9m\left(m+7\right)}{9m^2}=0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{128-64m+8m^2-9m^2-63m}{9m^2}=0\Leftrightarrow-m^2-127m+128=0\)(1)
Ta có: a+b+c=-1-127+128=0
=> PT (1) có 2 nghiệm \(m_1=1\left(nhận\right);m_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=\dfrac{128}{-1}=-128\left(nhận\right)\)
Vậy m=1;m=-128 thì pt đề cho có 2 nghiệm thỏa đề bài.
3. \(x^2+\left(4m+1\right)x+2\left(m-4\right)=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac=\left(4m+1\right)^2-4.1.\left[2\left(m-4\right)\right]=16m^2+8m+1-8m+32=16m^2+33>0\forall m\) => PT luôn có 2 nghiệm phân biệt với mọi m.
Theo Vi-ét, ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}S=x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=\dfrac{-\left(4m+1\right)}{1}=-4m-1\\P=x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=\dfrac{2\left(m-4\right)}{1}=2m-8\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có hpt: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-4m-1\\x_1x_2=2m-8\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-4m-1\\2x_1x_2=4m-16\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x_1+x_2+2x_1x_2=-17\)
cho PT x^2 -2(m+1)x+m^2+2=0(m là tham số).giải PT (1) với m=1
Khi m=1 thì pt sẽ là:
x^2-2*2x+1^2+2=0
=>x^2-4x+3=0
=>x=1 hoặc x=3